A balanced meal schedule plays a vital role in maintaining good health, supporting energy levels, and promoting overall well-being. Whether you are trying to lose weight, maintain a healthy lifestyle, or boost your energy, planning meals thoughtfully can make a significant difference. This article will explore what a well-organized meal schedule looks like, the benefits of sticking to one, and how you can design a plan that fits your individual needs.
Why Is a Meal Schedule Important?
Before diving into the details of the best meal schedule, it’s crucial to understand why having a meal routine is beneficial:
Boosts Metabolism: Eating at regular intervals helps to keep your metabolism active. This means your body continuously burns calories throughout the day.
Maintains Energy Levels: Consuming balanced meals spaced evenly ensures your body gets a steady supply of energy, preventing energy crashes or feelings of fatigue.
Helps With Weight Management: Regular eating habits reduce the chances of overeating, late-night snacking, or binge eating.
Regulates Blood Sugar Levels: For people with diabetes or those looking to maintain balanced blood sugar, a consistent meal schedule is key.
Now, let’s dive into how to structure your meal plan for optimal health.
SEE ALSO: What Protein Diet Is Good for Weight Loss?
How Many Meals Should You Eat in a Day?
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach to meal frequency, as it varies based on individual preferences, activity levels, and goals. However, most people benefit from eating three main meals a day, with some opting to include snacks in between. Below is a breakdown of a typical meal schedule:
Breakfast: Between 6:30 AM and 8:30 AM
Lunch: Between 12:00 PM and 2:00 PM
Dinner: Between 6:00 PM and 8:00 PM
Optional Snacks: Mid-morning (10:00 AM) and mid-afternoon (4:00 PM)
Let’s look at each meal in more detail.
Breakfast: The Most Important Meal of the Day
Why Is Breakfast Important?
Breakfast literally means “breaking the fast” after a night of sleep. A healthy breakfast jumpstarts your metabolism, providing you with energy and nutrients for the day ahead.
What Should a Healthy Breakfast Include?
A balanced breakfast should include:
- Protein: Eggs, Greek yogurt, or tofu to keep you feeling full.
- Carbohydrates: Whole grains like oatmeal or whole wheat toast for energy.
- Healthy Fats: Avocado, nuts, or seeds to support brain function and overall health.
- Fruits or Vegetables: These add fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
What Time Should You Eat Breakfast?
It’s best to have breakfast within one hour of waking up, ideally between 6:30 AM and 8:30 AM. This ensures your body starts functioning optimally early in the day.
Example Breakfasts:
- Scrambled eggs with whole grain toast and a side of fresh fruit.
- Oatmeal topped with almonds, chia seeds, and berries.
- A smoothie made with Greek yogurt, spinach, and banana.
Mid-Morning Snack: Refuel Before Lunch
Do You Need a Mid-Morning Snack?
Not everyone needs a mid-morning snack, but if you find yourself hungry a few hours after breakfast, it’s a good idea to have a small, nutrient-dense snack. This helps avoid overeating at lunchtime.
What Should a Healthy Mid-Morning Snack Include?
Your snack should include a combination of protein and fiber. These nutrients will keep you feeling full and energized.
Example Mid-Morning Snacks:
- An apple with almond butter.
- A handful of nuts or seeds.
- A small container of Greek yogurt with a sprinkle of granola.
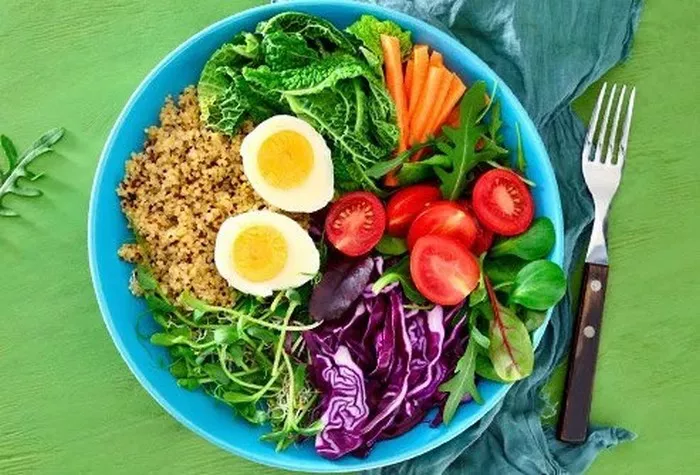
Lunch: Refueling Your Body for the Afternoon
Why Is Lunch Important?
Lunch is essential for keeping your energy levels steady throughout the afternoon. Skipping lunch or eating too little may lead to fatigue, poor concentration, and cravings later in the day.
What Should a Healthy Lunch Include?
A well-rounded lunch should have:
- Protein: Chicken, turkey, beans, or lentils for muscle repair and sustained energy.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Quinoa, brown rice, or sweet potatoes for slow-releasing energy.
- Vegetables: Leafy greens, tomatoes, cucumbers, or any other veggies to provide fiber and essential nutrients.
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil, avocado, or nuts for flavor and satiety.
What Time Should You Eat Lunch?
Lunch should be eaten about 4-5 hours after breakfast, typically between 12:00 PM and 2:00 PM.
Example Lunches:
- A quinoa salad with grilled chicken, avocado, and mixed greens.
- A whole grain sandwich with turkey, spinach, and a side of baby carrots.
- A lentil soup with a slice of whole grain bread.
Mid-Afternoon Snack: Keeping Your Energy Steady
Should You Have an Afternoon Snack?
Similar to the mid-morning snack, a mid-afternoon snack helps to maintain your energy until dinner. It can prevent overeating at dinner time and reduce cravings for sugary foods.
What Should a Healthy Afternoon Snack Include?
Choose a snack that provides a balance of protein, healthy fats, and fiber to satisfy your hunger.
Example Mid-Afternoon Snacks:
- A small handful of mixed nuts and dried fruit.
- Veggie sticks (carrots, celery) with hummus.
- Cottage cheese with cucumber slices.
Dinner: A Light But Nutritious Meal
Why Is Dinner Important?
Dinner replenishes your body’s nutrient reserves and helps you wind down for the day. However, it’s crucial to avoid heavy, high-calorie meals at night as they can interfere with sleep.
What Should a Healthy Dinner Include?
Dinner should be lighter than lunch but still provide adequate nutrition. A balanced dinner includes:
Protein: Fish, chicken, or plant-based sources like tempeh.
Vegetables: Roasted, steamed, or fresh vegetables for fiber and vitamins.
Whole Grains or Starchy Vegetables: Brown rice, sweet potatoes, or whole grain pasta for energy.
What Time Should You Eat Dinner?
It’s best to have dinner at least 2-3 hours before bedtime, usually between 6:00 PM and 8:00 PM. This gives your body time to digest the food before you sleep.
Example Dinners:
- Grilled salmon with roasted vegetables and quinoa.
- Stir-fried tofu with mixed vegetables and brown rice.
- A vegetable soup with a side of whole grain toast.
Should You Eat Late at Night?
Is Eating Late Bad for You?
Eating late at night is often linked to weight gain and poor digestion. If you do find yourself feeling hungry before bed, try to opt for a small, light snack rather than a full meal.
What Are Good Late-Night Snack Options?
If you need something before bed, choose foods that are easy to digest and won’t interfere with your sleep.
Example Late-Night Snacks:
- A small banana with a tablespoon of peanut butter.
- A handful of almonds.
- A cup of herbal tea with a few whole grain crackers.
The Importance of Hydration
How Much Water Should You Drink?
While planning your meals, it’s equally important to stay hydrated. Drinking water throughout the day supports digestion, maintains energy levels, and keeps your skin healthy. Aim for at least 8 cups of water per day, more if you are physically active.
Best Times to Drink Water:
- Upon waking up.
- Before and after meals.
- Throughout the day to stay hydrated.
Tips for Sticking to a Meal Schedule
Creating the perfect meal schedule is one thing, but sticking to it is another. Here are some tips to help you maintain a regular eating pattern:
Meal Prep: Plan and prepare meals ahead of time to avoid last-minute unhealthy food choices.
Listen to Your Body: While it’s good to stick to a schedule, listen to your hunger and fullness cues. Eat when you’re hungry and stop when you’re satisfied.
Avoid Skipping Meals: Skipping meals can lead to overeating later. Always try to eat something, even if it’s a small snack.
Keep Healthy Snacks on Hand: Always have healthy options available to prevent reaching for junk food.
Set a Reminder: If you often forget to eat on time, set reminders on your phone or calendar.
Conclusion
The best meal schedule is one that fits your lifestyle, supports your energy needs, and helps you maintain a balanced, healthy diet. Generally, eating three main meals per day—breakfast, lunch, and dinner—with optional snacks, is a good approach. Remember to include a balance of protein, healthy fats, and carbohydrates in each meal, and stay hydrated throughout the day. With a little planning and consistency, you can create a meal schedule that works for you and supports your health goals.
Related topics: